Understanding Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of a Healthy Diet
Understanding Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of a Healthy Diet
Introduction
When we think about nutrition, the first thing that often comes to mind is calories, but it’s not just about how many calories we eat—it’s about the quality and source of those calories. That’s where macronutrients come into play. These are the nutrients that provide energy (calories) to our bodies and are essential for various functions, from building muscles to supporting our immune systems. The three main macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—are the foundation of any well-rounded diet.
But with so many dietary trends and conflicting information out there, it can be hard to know what to believe. Do carbs make you gain weight? Is protein the secret to a lean body? Should you avoid fats altogether? Let’s explore each macronutrient in detail to understand their roles and how to incorporate them into a healthy diet.Understanding Macronutrients
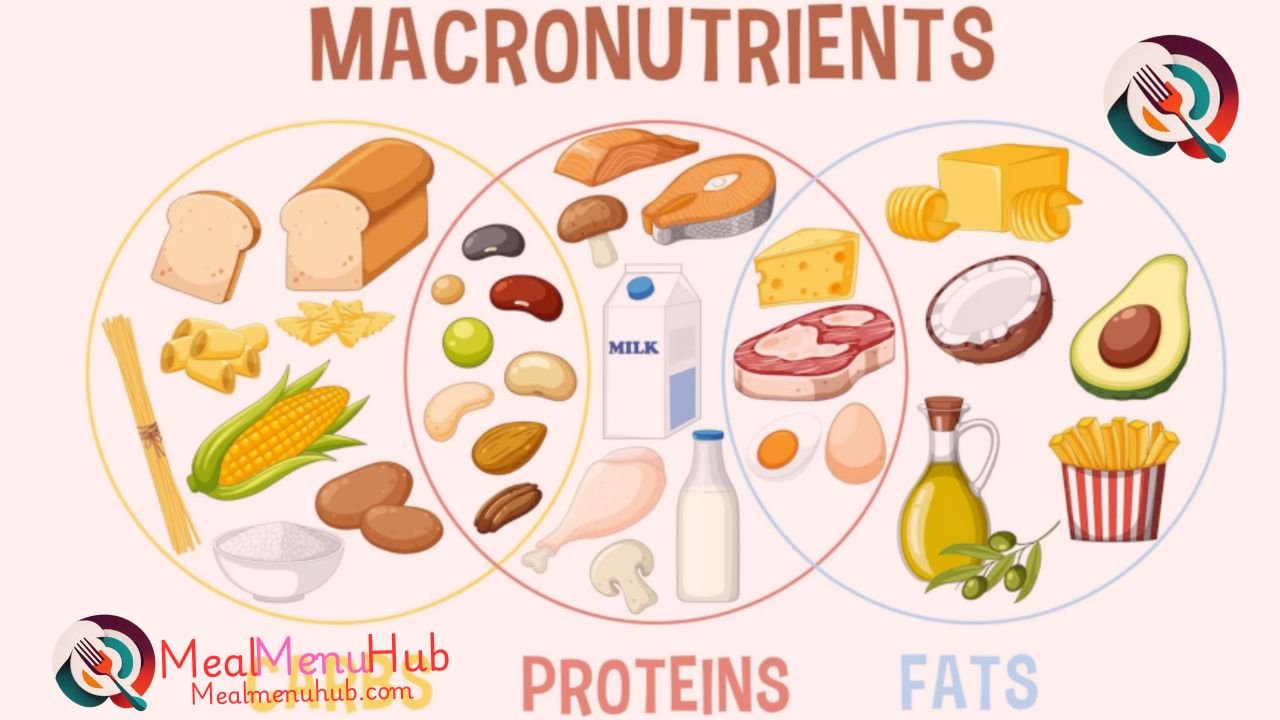
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients that our body needs in large amounts to provide energy and support basic bodily functions. Unlike micronutrients (such as vitamins and minerals), which we need in smaller quantities, macronutrients are the building blocks of a healthy diet.
There are three primary macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
Each of these macronutrients plays a different but equally important role in maintaining our overall health, supporting our metabolism, and fueling our day-to-day activities.
Carbohydrates: Your Body’s Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body’s main energy source. When we consume carbs, our body breaks them down into glucose (sugar), which is used for fuel by our muscles, brain, and other tissues.Understanding Macronutrients
Types of Carbohydrates:
- Simple Carbohydrates: Found in foods like fruits, dairy, and refined sugars. These are broken down quickly by the body and provide fast energy. However, they can also lead to blood sugar spikes if consumed in large amounts.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Found in foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. These are digested more slowly and provide long-lasting energy.Understanding Macronutrients
Healthy Sources of Carbs:
- Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa
- Vegetables such as sweet potatoes and broccoli
- Legumes like lentils and beans
- Fruits like apples, berries, and bananas
Proteins: The Building Blocks of Your Body
Proteins are essential for the repair and growth of muscles, tissues, and cells. They also play a crucial role in enzyme production, immune function, and hormone regulation. In fact, protein is involved in nearly every bodily process, making it an essential part of a balanced diet.Understanding Macronutrients
The Role of Protein:
- Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein is key for repairing muscles after exercise and supporting new muscle growth.
- Immune Function: Many components of the immune system, such as antibodies, are made from proteins.
- Enzyme Production: Enzymes that help in digestion, metabolism, and many other processes are made from proteins.
Best Sources of Protein:
- Lean meats like chicken and turkey
- Fish and seafood
- Plant-based sources like beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa
- Dairy products like Greek yogurt and cottage cheese
- Understanding Macronutrients
Fats: Essential for Health and Energy
Fats are often misunderstood, but they are just as essential to a healthy diet as carbohydrates and protein. In fact, fats are necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and the production of hormones. Fats are also a concentrated source of energy, providing more than twice the number of calories per gram as carbohydrates and proteins.Understanding Macronutrients
Types of Fats:
- Saturated Fats: Found in animal products like fatty cuts of meat, butter, and dairy. These should be consumed in moderation.
- Unsaturated Fats: Found in plant-based oils (like olive oil), nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. These are considered “healthy” fats and can help improve heart health.
- Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods, these fats are harmful to your health and should be avoided.Understanding Macronutrients
Healthy Fat Sources:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds)
- Olive oil and coconut oil
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
How Much of Each Macronutrient Do You Need?
The right macronutrient balance varies depending on your individual needs, such as your activity level, fitness goals, and health condition.
- General Guidelines:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of your total daily calories
- Proteins: 10-35% of your total daily calories
- Fats: 20-35% of your total daily calories
To determine how much of each macronutrient you need, you can calculate your daily caloric intake based on your goals (e.g., weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance) and adjust the ratios accordingly.Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrient Ratios and How They Affect Your Health
Different macronutrient ratios can have various effects on your health. For example, some people may benefit from a higher protein intake for muscle building, while others may focus on healthy fats for better heart health.
- Low-Carb Diets: Often used for weight loss and improving insulin sensitivity.
- High-Protein Diets: Common for athletes or individuals looking to build muscle mass.
- High-Fat, Low-Carb Diets (Keto): Used for weight loss and improving fat burning.
The Importance of Fiber: A Key Carbohydrate
Fiber, while a type of carbohydrate, doesn’t get digested by the body. However, it plays a crucial role in digestion, gut health, and preventing constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Both are necessary for maintaining good digestive health.Understanding Macronutrients
- Soluble Fiber: Found in oats, apples, and beans, it helps lower blood cholesterol and stabilize blood sugar.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in whole grains, vegetables, and nuts, it helps move food through the digestive system.
The Impact of Processed Foods on Macronutrient Intake
Processed foods are often stripped of their nutrients and can disrupt your macronutrient balance. These foods are often high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and empty calories, which can lead to weight gain, blood sugar imbalances, and chronic health conditions. By choosing whole foods, you ensure that you’re getting the most out of your macronutrient intake.Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients and Weight Management
The right balance of macronutrients can be a key factor in managing weight. Protein, in particular, is helpful for weight management because it helps control hunger and boosts metabolism. Carbohydrates and fats also play a role in energy balance, making it essential to find the right proportions for your goals.
Conclusion
Understanding macronutrients is the first step toward a healthier, more balanced diet. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats all play unique roles in supporting energy, muscle growth, digestion, and overall health. By ensuring your diet includes a proper balance of these macronutrients, you’ll be fueling your body for optimal performance, health, and well-being.
FAQs
- What are the three main macronutrients?
- The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays an essential role in providing energy and supporting overall health.
- How much of each macronutrient should I eat?
- General guidelines suggest that 45-65% of your daily calories come from carbohydrates, 10-35% from protein, and 20-35% from fats. However, your needs may vary depending on your goals.
- Are fats bad for you?
- Not all fats are bad. Healthy fats, like unsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are crucial for heart health. It’s the unhealthy fats (trans fats and too much saturated fat) that you should limit.
- Can I lose weight on a low-carb diet?
- Yes, many people find success with low-carb diets for weight loss. Reducing carbohydrate intake can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce calorie intake, leading to fat loss.
- Why is protein important for muscle building?
- Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. After exercise, consuming adequate protein helps repair muscle fibers, which is necessary for building lean muscle mass.
- Contact Us